The U.S. semiconductor manufacturing industry is experiencing a significant resurgence, driven by substantial investments and strategic initiatives aimed at bolstering domestic production. This renewed focus addresses supply chain vulnerabilities and aims to reduce reliance on foreign sources for critical components.
Current Landscape of U.S. Semiconductor Manufacturing
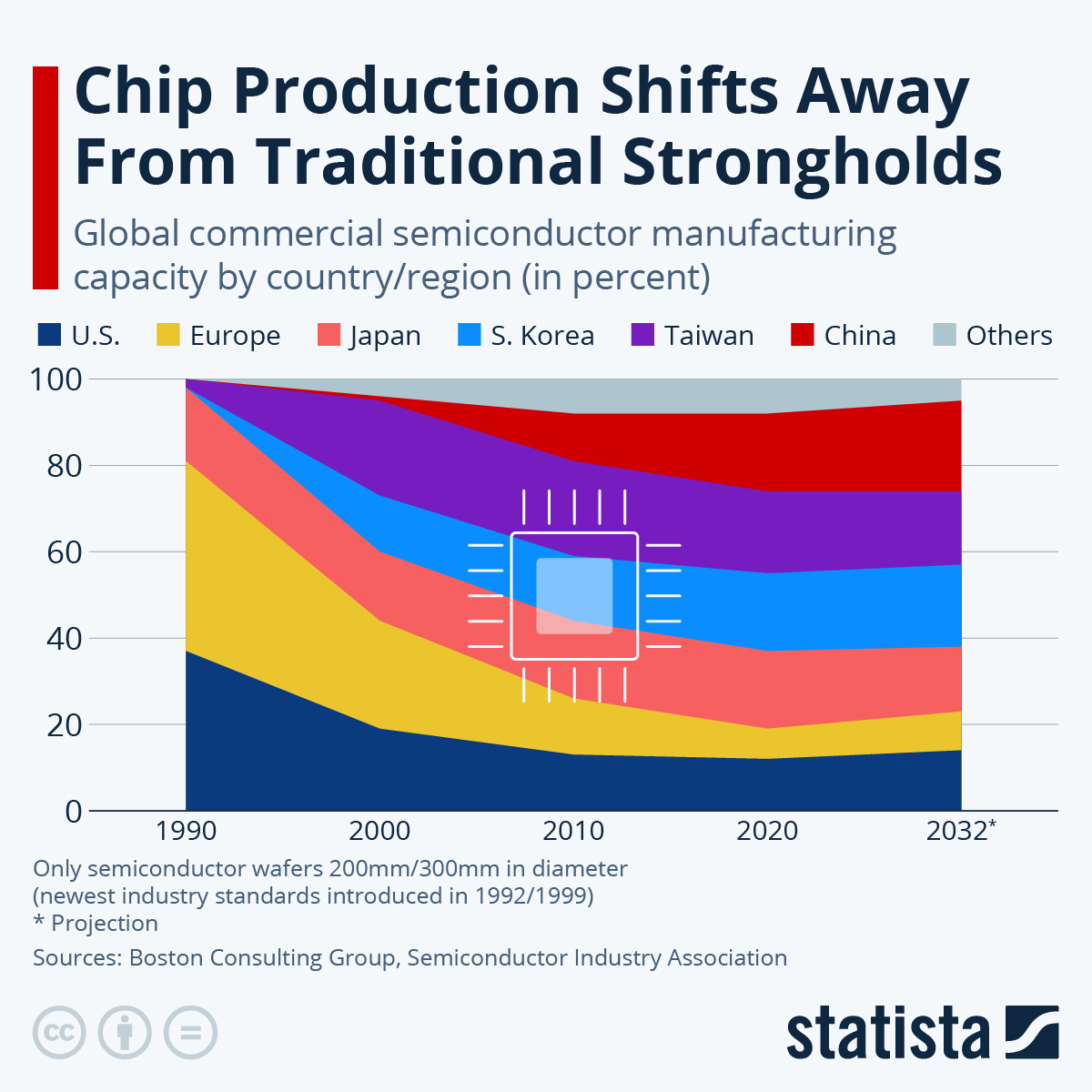
Historically, the United States was a leader in semiconductor manufacturing, but its share of global production capacity declined from 37% in 1990 to about 10% in 2022. To reverse this trend, the U.S. government enacted the CHIPS and Science Act in 2022, allocating $280 billion to stimulate domestic semiconductor production. This initiative is projected to create approximately 93,000 construction jobs and 43,000 permanent positions in the semiconductor sector (1).
The graph on the left illustrates the projected revenue growth in the U.S. semiconductor market from 2025 to 2029, highlighting an expected annual growth rate of 8.05%. The CHIPS Act, along with private investments, is set to accelerate this growth.
Major Investments by Leading Semiconductor Companies
Intel announced an initial $20 billion investment to establish new fabrication plants in Ohio, with plans to expand up to $100 billion—the largest investment in the state's history.
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) is constructing a $12 billion facility in Arizona, expected to be operational by 2025, significantly expanding the U.S.'s capacity in advanced chip manufacturing.
Samsung plans to build a $17 billion semiconductor factory in Texas, aiming to commence operations in the latter half of 2024.
Challenges and Opportunities in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Despite these advancements, the industry faces several challenges:
- Shortage of Skilled Labor: The semiconductor industry requires highly trained professionals, and the U.S. educational pipeline has struggled to meet this demand.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty: Trade policies and international relations with China and Taiwan continue to impact the semiconductor supply chain.
- High Capital Costs: Semiconductor fabs require billions of dollars in investments, making it difficult for new entrants.
The chart above shows the global market distribution of semiconductor sales. The U.S. remains a key player, but Asia dominates the sector, particularly China, Taiwan, and South Korea. The CHIPS Act is an effort to rebalance the global share. Source: SEMI Market Trends Report
3D-Printed PCBs in Manufacturing
In parallel with traditional semiconductor manufacturing, 3D-printed electronics are gaining traction, particularly for rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing. 3D-printed PCBs eliminate the need for traditional etching processes and provide manufacturers with on-demand production capabilities.
How 3D-Printed PCBs Are Transforming Manufacturing
- Faster Prototyping: Startups, research institutions, and R&D teams can rapidly iterate new PCB designs without waiting weeks for manufacturing.
- Cost Reduction: Traditional PCB manufacturing involves expensive photolithography and etching, whereas 3D-printed PCBs use additive manufacturing techniques, reducing waste and costs.
- Flexibility in Design: Unlike conventional PCBs, 3D-printed electronics allow multi-layered, flexible, and even stretchable circuits, opening doors for applications in wearables, medical devices, and aerospace.
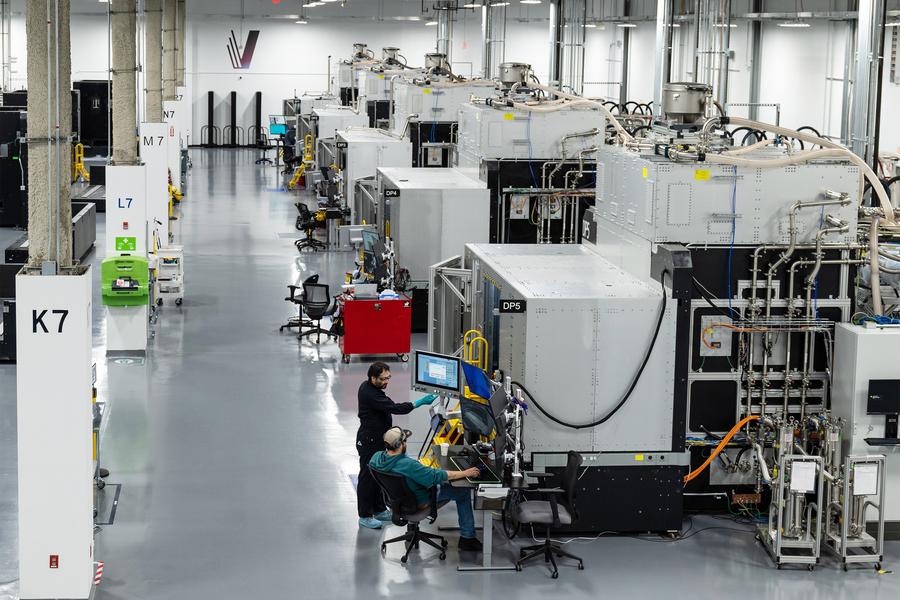

The image on the left showcases a cutting-edge 3D printing manufacturing facility, representing the evolution of additive manufacturing in industrial-scale production. Companies like VulcanForms are leading the transition of 3D printing from prototyping into full-scale manufacturing, demonstrating the potential of advanced digital production in various industries, including semiconductor and PCB fabrication. (Source: MIT News)
Companies Leading the 3D-Printed PCB Revolution
Several companies are driving 3D-printed PCB innovation, including:
- Nano Dimension – Specializes in industrial-scale 3D PCB printing for high-performance applications.
- BotFactory – Provides desktop 3D PCB printers, enabling engineers to print, assemble, and test circuit boards in minutes.
- Voltera – Develops 3D PCB printers focused on flexible and experimental electronics.
Real-World Applications
- NASA & Aerospace: 3D-printed PCBs are used in satellite technology and space exploration, where on-demand electronics production is critical.
- Defense & Military: The U.S. Air Force has partnered with BotFactory and other firms to develop electronics in the field without relying on external supply chains.
- Medical Devices: 3D-printed PCBs enable wearable health monitoring devices, a rapidly growing industry.
Conclusion
As the United States endeavors to revitalize its semiconductor manufacturing sector, the contributions of 3D-printed electronics and PCBs are increasingly vital. These new technologies streamline R&D, reduce costs, and enable flexible, high-performance circuit design.
